I. Introduction
II. History of Lie Detector Tests
III. How Lie Detector Tests Work
IV. Accuracy of Lie Detector Tests
V. Admissibility of Lie Detector Tests in Court
VI. Arguments for and Against the Admissibility of Lie Detector Tests in Court
VII. Recent Developments in the Admissibility of Lie Detector Tests in Court
VIII. Conclusion
IX. FAQ
X. Resources
| Feature | Lie Detector Test | Court | Admissible | Credibility | Polygraph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Introduction | A lie detector test, also known as a polygraph test, is a device used to measure physiological changes in a person’s body in order to determine if they are telling the truth. | The use of lie detector tests in court is controversial. Some jurisdictions allow lie detector tests to be used as evidence, while others do not. | The admissibility of lie detector tests in court varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. In some jurisdictions, lie detector tests are not admissible at all. In other jurisdictions, lie detector tests may be admissible, but only under certain conditions. | The credibility of lie detector tests is a topic of debate. Some people believe that lie detector tests are accurate and reliable, while others believe that they are not. | The polygraph is a type of lie detector test. It is a device that measures physiological changes in a person’s body, such as heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure, in order to determine if they are telling the truth. |
II. History of Lie Detector Tests
Lie detector tests have been used in the United States since the early 1900s. The first lie detector test was developed by a psychologist named John Larson in 1921. Larson’s lie detector test was based on the principle that changes in a person’s physiological responses, such as heart rate and blood pressure, can indicate when they are lying.
In the early years, lie detector tests were used primarily by law enforcement officials. However, in the 1950s, lie detector tests began to be used in the workplace as well. By the 1970s, lie detector tests were being used in a variety of settings, including schools, banks, and hospitals.
In the 1980s, the use of lie detector tests in the workplace came under scrutiny. Critics argued that lie detector tests were not reliable and that they could be used to discriminate against certain groups of people, such as minorities and women. As a result, a number of states passed laws limiting the use of lie detector tests in the workplace.
Today, the use of lie detector tests is still controversial. There is no consensus on whether lie detector tests are reliable or whether they should be used in the courtroom or the workplace.
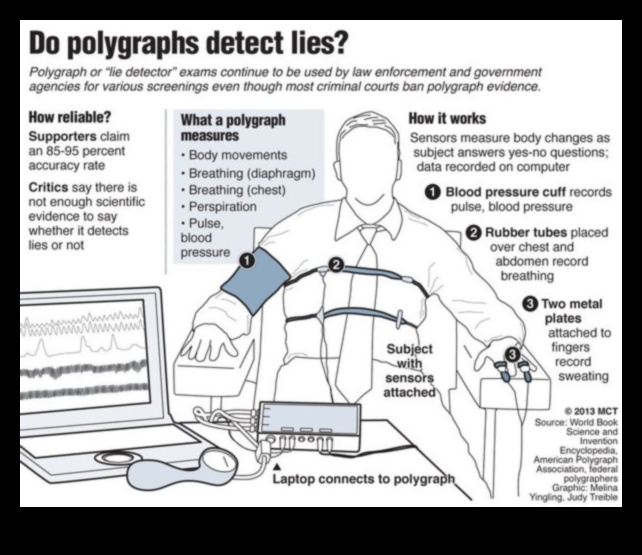
III. How Lie Detector Tests Work
Lie detector tests, also known as polygraph tests, measure physiological changes in the body that are associated with deception. These changes include changes in heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, and skin conductance. When a person lies, they experience a stress response that causes these physiological changes. Lie detector tests can detect these changes and indicate when a person is lying.
Lie detector tests are not 100% accurate. There are a number of factors that can affect the results of a lie detector test, including the person’s level of anxiety, their ability to control their bodily responses, and the skill of the examiner. For this reason, lie detector tests should not be used as the sole basis for making decisions about a person’s guilt or innocence.

V. Admissibility of Lie Detector Tests in Court
The admissibility of lie detector tests in court is a complex and controversial issue. There are a number of factors that courts consider when determining whether to admit a lie detector test as evidence, including:
- The scientific validity of lie detector tests
- The reliability of lie detector tests
- The prejudicial impact of lie detector tests
- The availability of other, more reliable evidence
In general, courts have held that lie detector tests are not admissible in court as evidence because they are not sufficiently reliable. However, there are a few exceptions to this rule. For example, lie detector tests may be admissible in court if they are used for impeachment purposes, or if the parties have agreed to the admission of the test results.
The admissibility of lie detector tests in court is an evolving area of law. As the science of lie detection continues to develop, courts may become more willing to admit lie detector tests as evidence. However, it is important to note that the admissibility of lie detector tests in court is still a matter of debate, and there is no guarantee that a lie detector test will be admitted as evidence in any particular case.
V. Admissibility of Lie Detector Tests in Court
The admissibility of lie detector tests in court is a complex and controversial issue. There are a number of factors that courts consider when determining whether to admit a lie detector test into evidence, including:
- The scientific validity of lie detector tests
- The reliability of lie detector tests
- The prejudicial effect of lie detector tests
- The availability of other, more reliable forms of evidence
In general, courts have been reluctant to admit lie detector tests into evidence, due to concerns about their scientific validity and reliability. However, there are a few exceptions to this rule. For example, some courts have allowed lie detector tests to be admitted into evidence when they are used to corroborate other forms of evidence, or when they are used to impeach a witness’s testimony.
The admissibility of lie detector tests in court is an evolving area of law. As the science of lie detection continues to develop, courts may become more willing to admit lie detector tests into evidence. However, it is important to note that the admissibility of lie detector tests is still a matter of debate, and there is no guarantee that a lie detector test will be admitted into evidence in any particular case.

VI. Arguments for and Against the Admissibility of Lie Detector Tests in Court
There are a number of arguments for and against the admissibility of lie detector tests in court. Some of the arguments in favor of admissibility include:
- Lie detector tests are scientifically valid and reliable.
- Lie detector tests can help to protect the innocent and convict the guilty.
- Lie detector tests can save time and money by helping to resolve cases quickly.
Some of the arguments against admissibility include:
- Lie detector tests are not 100% accurate.
- Lie detector tests can be biased against certain groups of people.
- Lie detector tests can be used to intimidate or coerce suspects into giving false confessions.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to admit lie detector tests in court is a complex one that must be made on a case-by-case basis.
VII. Recent Developments in the Admissibility of Lie Detector Tests in CourtIn recent years, there have been a number of developments in the admissibility of lie detector tests in court. These developments include:
- In 2004, the Supreme Court ruled in Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals, Inc. that the Federal Rules of Evidence superseded the Frye standard for admitting expert testimony. This ruling made it easier for plaintiffs to admit lie detector test evidence in federal court.
- In 2009, the American Psychological Association (APA) issued a revised set of guidelines for the use of lie detector tests in forensic settings. These guidelines included a number of recommendations for improving the accuracy and reliability of lie detector tests.
- In 2012, the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) released a report on the scientific status of lie detector tests. The NAS report concluded that lie detector tests are not reliable enough to be used in court.
- In 2018, the U.S. Department of Justice issued a policy statement on the use of lie detector tests in federal law enforcement. The policy statement prohibited the use of lie detector tests for pre-employment screening and limited their use in other investigative settings.
These developments have had a significant impact on the admissibility of lie detector tests in court. While some courts have continued to admit lie detector test evidence, others have been more reluctant to do so. The overall trend is for courts to be more cautious about admitting lie detector test evidence, and it is likely that this trend will continue in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the admissibility of lie detector tests in court is a complex and controversial issue. There are a number of factors to consider when determining whether or not a lie detector test is admissible, including the type of test, the circumstances under which the test was administered, and the reliability of the test results. While some courts have held that lie detector tests are admissible, others have found that they are not. The Supreme Court has not yet ruled on the issue of lie detector test admissibility, and it is likely that the Court will not do so in the near future. As a result, the admissibility of lie detector tests in court remains a matter of state law.
IX. FAQ
What is a lie detector test?
A lie detector test, also known as a polygraph test, is a test that measures physiological changes in a person’s body in order to determine if they are lying.
How does a lie detector test work?
A lie detector test measures changes in a person’s heart rate, breathing rate, and perspiration level. These changes are caused by the stress of lying.
How accurate are lie detector tests?
Lie detector tests are not 100% accurate. The accuracy of a lie detector test depends on a number of factors, including the skill of the examiner, the condition of the equipment, and the cooperation of the person being tested.
Are lie detector tests admissible in court?
The admissibility of lie detector tests in court varies from state to state. In general, lie detector tests are not admissible as evidence in court because they are considered to be unreliable.
What are the arguments for and against the admissibility of lie detector tests in court?
There are a number of arguments for and against the admissibility of lie detector tests in court. Some of the arguments in favor of the admissibility of lie detector tests include:
- Lie detector tests can help to protect the innocent by identifying people who are lying.
- Lie detector tests can help to convict criminals by providing evidence of their guilt.
- Lie detector tests can deter crime by making people think twice about lying.
Some of the arguments against the admissibility of lie detector tests in court include:
- Lie detector tests are not 100% accurate.
- Lie detector tests can be biased against certain groups of people.
- Lie detector tests can be used to intimidate or coerce people into giving false confessions.
What are the recent developments in the admissibility of lie detector tests in court?
In recent years, there have been a number of developments in the admissibility of lie detector tests in court. Some of these developments include:
- The Supreme Court has ruled that lie detector tests are not admissible as evidence in federal court.
- A number of states have passed laws that restrict the use of lie detector tests in employment settings.
- A number of companies have stopped using lie detector tests in their hiring process.
Q: What is a lie detector test?
A: A lie detector test, also known as a polygraph test, is a type of psychological test that is used to measure a person’s physiological responses to questions that are asked by a trained examiner. The goal of a lie detector test is to determine whether a person is telling the truth or lying.
Q: Are lie detector tests admissible in court?
A: The admissibility of lie detector tests in court varies from state to state. In some states, lie detector tests are admissible as evidence, while in other states, they are not. The decision of whether or not to admit a lie detector test as evidence is ultimately up to the judge.
Q: What are the limitations of lie detector tests?
Lie detector tests are not perfect. There are a number of factors that can affect the accuracy of a lie detector test, including the person’s level of anxiety, their ability to control their physiological responses, and the skill of the examiner.